AI-Generated Text vs. AI-Assisted Tools
Not all AI tools are created equal—and in higher education, that difference matters.
AI-generated text tools can write full sentences, paragraphs, or even entire assignments for you. Since the work comes from the AI and not you, using it for graded assignments violates the academic integrity policy.
AI-assisted tools, on the other hand, are like a helpful guide. They won’t do your work for you, but they can give you a starting point—sparking ideas, guiding your research, or helping you organize your thoughts. You’re still doing the thinking and writing, which is why these tools are generally okay to use when you follow your instructor’s guidelines.
Quick Comparison
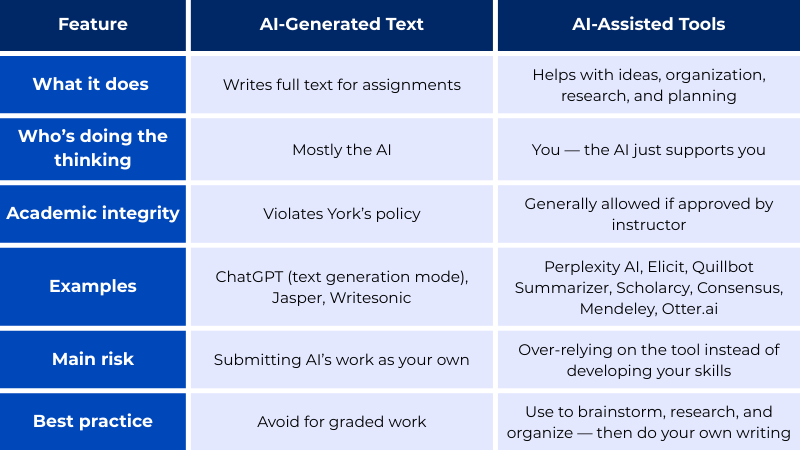
If the AI is doing the writing for you, it’s not your work.
Examples of AI-Assisted Programs